Hybrid Cloud Benefits
Organizations adopting this architectural approach gain access to unparalleled scalability, allowing them to rapidly adjust computing resources based on fluctuating demand without significant capital investments in physical hardware. The model delivers enhanced security by enabling companies to retain their most sensitive data and mission-critical applications within private, controlled environments while still leveraging public cloud capabilities for less sensitive operations.
The flexibility inherent in this dual-environment strategy empowers businesses to make strategic decisions about workload placement based on regulatory requirements, performance needs, and security considerations. This approach eliminates the traditional trade-off between security and agility, enabling organizations to maintain strict data governance while benefiting from the innovation and rapid deployment capabilities that public cloud services provide.
Cost and Performance Optimization
Financial efficiency drives much of the appeal behind this dual-cloud strategy, as businesses can strategically allocate their most cost-sensitive workloads to public cloud environments where they pay only for consumed resources, while maintaining expensive on-premises infrastructure exclusively for high-security or performance-critical applications. This selective approach prevents over-provisioning of costly hardware and reduces total cost of ownership by eliminating the need to build internal capacity for peak demand scenarios.
Performance optimization occurs through intelligent workload distribution, where latency-sensitive applications remain close to users on local infrastructure while compute-intensive tasks that benefit from elastic scaling can leverage the virtually unlimited resources available through public cloud providers. The result is a balanced architecture that maximizes both operational efficiency and cost control without compromising on security or performance requirements.
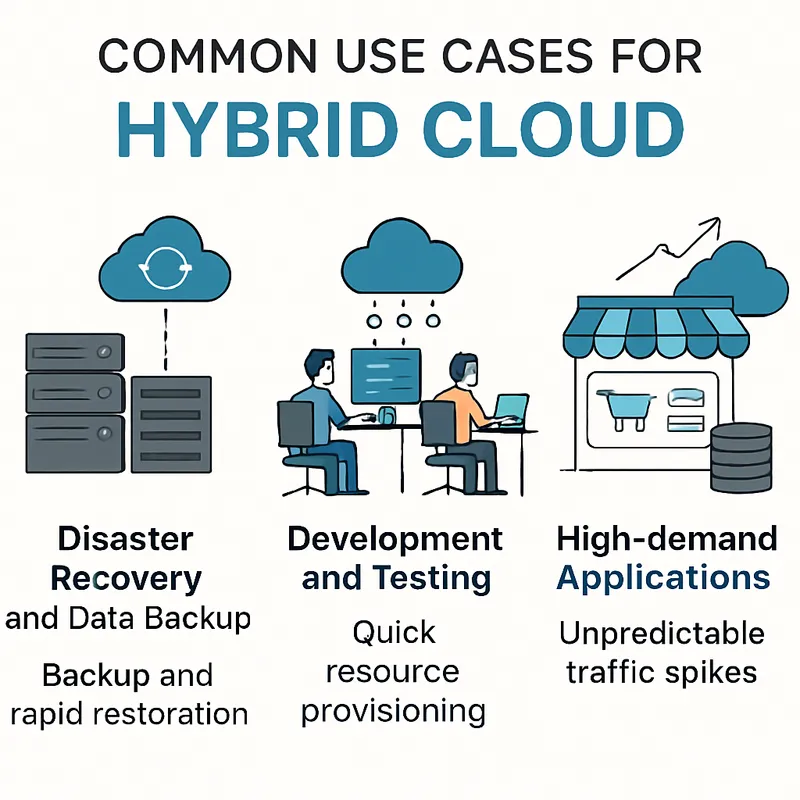
Common Use Cases
Disaster recovery and data backup represent the most widely adopted implementations, where organizations store critical backup data in public cloud environments to ensure rapid restoration capabilities while maintaining production systems on-premises. Development and testing environments frequently leverage this model, allowing engineering teams to spin up resources quickly in the public cloud for prototyping and experimentation while keeping production workloads secure within private infrastructure.
High-demand applications that experience unpredictable traffic spikes benefit significantly from this approach, as businesses can seamlessly burst into public cloud resources during peak periods—such as e-commerce sites during holiday seasons or streaming services during major events—while maintaining baseline operations on their own infrastructure. Regulatory compliance scenarios also drive adoption, where organizations must keep certain data types within specific geographic boundaries or under direct control while still accessing cloud services for other business functions.